Abstract: A block chain is a public ledger of data collected within a network that sits on top of the internet. It is how this data is recorded that gives block chain its ground22breaking potential. The BC-Block chain skill is usually associated with Bit-coin and other crypto-Currencies, but that is just the angle of the iceberg. Some citizens think block-chain might end up modifying a number of significant applications, from health-care to government. Block-chain technology is an apparently simple invention that has immense applications reaching across global business and human civilization. There may be a future where consumers benefit from the features of a block chain without even considering it, much like how every corner of daily life now has been integrated by internet. This study represents what is blockchain technology, how does BC works, Advantages and disadvantages and Implementation of BC using Java. Index Terms: Blockchain Technology how does BC works, Advantages and disadvantages, Implementation of BC
I. INTRODUCTION
The blockchain technology is a safe shared Electronic ledger, linking several communities in a network of belief and integrity, expedite the relocation of belongings and the data concerning to those belongings. It was initially developed as the means through which Bitcoin could be proved as correct electronic currency after the unstable events in the financial world that paved the way to the Global financial alteration in 2008. It uses a sequential chain using cryptographic digital keys for the reliable recorded digital transactions, which are confirmed by the network as correct. Repetition, modification or deletion of transactions is stopped by the chain, which is incorporated on everyone’s system on the network. Longer Blockchain and the wider network, complexed digital key are the features of the most reliable blockchain. The best use of blockchain is in a decentralized fashion where it is simply a shared ledger. The blockchain increases in a chain format which is made up of several blocks. Every block has the information which describes the block present before it in the blockchain. A unique ID which in the like text combination is the cryptographic hash which is developed by considering the given parameters:
The blockchain is significant as it generates confidence in peer to peer networks. Banks are the trusted third party for transactions it is why they are present. For an example suppose there were no banks and we were forced to exchange the goods hand in hand how can we confirm that the other person is authentic. Suppose if the person gives salt in place of sugar, or give degraded quality sugar how can we find this fraud Let’s see an example. Blockchain technology is the answer. Now we have a third party which we trust for our transactions and this is using blockchain technology. Bitcoin mining points to the process through which new Bitcoins are generated and given to computers helping to support the network. The process of the computational race to concoct new transactions coming onto the network because of the computers involved in Bitcoin mining. Now as the technology behind Bitcoin is Blockchain its demand has increased. It is commonly seen that people consider bitcoin and blockchain similarly. But the applications of blockchain are more than the bitcoin. Any type of information can be contained in the blocks of blockchain therefore it is a technology which is highly useful and versatile. Blockchain database can contain data like car tiles, medical records etc. In case when we need to keep data in conditions like it should not be altered, it should be secure, open to the user and decentralized then blockchain is useful. Some more use-cases include: To reiterate the arguments pertaining to the technical side, data which is stored using a blockchain data structure is change-resistant, as after developing a block it will be required to modify all the blocks after it. If one previous block is made, all subsequent blocks are modified with respect to their hashes as a consequence. Hence, it is not possible to change in any block to without verifying it. After Bitcoin was introduced blockchain to the world then primarily three types of Blockchains that have developed. Public-permissioned blockchain, private-permissioned blockchain etc. are some of the more complicated types but we will discuss the simple one’s here. Let’s see all the three turn by turn.
Public Blockchain: They are discussed as permission less ledgers that is, they contain no boundations. With all participants containing a similar copy of the ledger they allow anyone to enter data to the ledger. This methodology is added suitable for censorship-resistant applications (e.g. Bitcoin) as there is no individual owner of it. Public Blockchains mostly allow considerations with regards to economy for those who work for the security of the network. Private Blockchain: They are also known as permission ledgers, as they only allow the participants who join by an invite to the network. These networks are under the administration of either a single or a number of network administrators who are nominated by the network. Private blockchains has provision for sharing similar copies of a ledger, but only to a specific number of participants that too trusted only. This methodology is more adaptable for applications requiring simplicity, speed, and greater transparency as the network may have an owner(s), Hybrid Blockchain: They are also known as consortium blockchains, they are considered to have properties of both public and private blockchains and even it is found to be semi-decentralized. Both the properties can be seen as it has set of permissions which resemble private blockchains, but there is a single firm or a group or firms which has control over it. Administers of each firm can fix the number if users’ reading rights on their wish and only allow a particular number of trusted nodes to perform a consensus protocol.
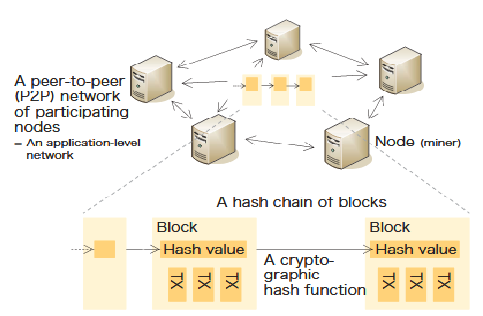
In previous days, one of the most widely emerging fields of computer science are cryptocurrencies and blockchain applications, leading to strong requirement for software applications. A number of new projects were introduced in daily basis and with a very positive result. But there were very big fails and disasters due to lack of experience and market time like those of DAO in 2016 and of Parity Ethereum wallet in 2017. MtGox in 2014 (350 million US$), Bitfinex in 2016 (72 million US$), and Coincheck in 2017 (400 million US$) are the hacks operated on exchanges of cryptocurrency. The success of this filed can be considered by the development of sound SE practices to blockchain development in both the generic and smart contract. Here the issues are the need for specific analysis and design methods, quality control through testing and metrics, security assessment and overall development process.[1] Named Data Networking is developed with security wherein it is required that digital signature is attached to every named Data object by the producer. To verify that the data packet is not affected by changing the content in it the project has incorporated a testbed. But two challenges are present in this model for verifying fake content: (1) As it is an architecture which is governed by the central authority it tends to fail and as the central point fails it is not possible to check on the network which key was incorrect. and (2) there is a lot of extra resources required to verify the signature when the certificate is taken across various nodes. 2] The blockchain is a new technology for data sharing between untrusted peers. However, it does not work well with extensive transactions. Besides, there are high barriers between various blockchain systems. Interactive multiple blockchain architectures is an innovative component-based framework for exchanging information across arbitrary blockchain system . In our architecture, a dynamic network of multi-chain is created for inter-blockchain communication.[3] Blockchain technology faces several challenges when we build them on existing systems rather than from scratch. It is difficult to find out which attributes of blockchains are important for a given use case (e.g. immutable, trustless, anonymous) and to decide which elements of architecture should employ blockchain technologies. Current approaches generally only give a hint on whether blockchain technology makes sense for a given use case or not [4]. The blockchain is not only restricted to cryptocurrency it is expanding its applications as it is trusted by users even though it has no centralized organization like government as shown in Figure 1. Figure1: A blockchain depicted as a distributed system Fundamental problem with public blockchain is the reason behind the mismatch. The nodes that support blockchain has incentive based on economy like gaining coins which is different for other applications of blockchain. If the following blockchain collapses due to the lack of motivation for economy the upper layer cannot continue. It is the old concept to align the node and application incentive of blockchain and hence is still a problem. . It is non-trivial to align the blockchain node and application incentives, and this is still an open problem.[5]. Blockchain and the Internet of Things (IoT) are main technologies which in the coming 10 years will have a vast influence in the industrial sector. This article describes how these two technologies will advance proficiency, provide new business opportunities, address regulatory requirements, and improve clearness and visibility.[6] Privacy, assured by the integration of cryptography and decentralization, is one of the main reasons for the usage of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. But the privacy assured by Bitcoin is not up to the mark hence there is a shift to privacy-centric blockchains, most users of blockchain remain responsive to privacy attacks that angered network-layer information and access patterns that leak as users interact with blockchains. Recognizing if and how blockchain-based applications can provide strong privacy guarantees is a matter of increasing urgency.[7]
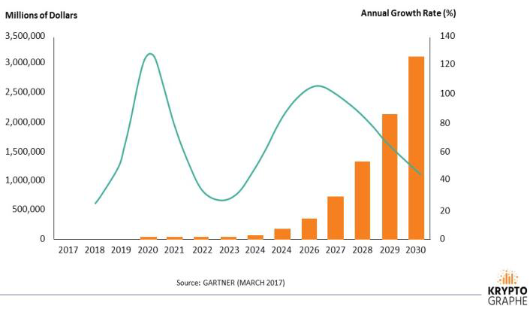
The basic conception of a blockchain is quite simple: it is a 1. Shared, redundant log file (sometimes called a ledger). 2.The entries are required to be one after the other and should be time-stamped. 3.There is a one way function which generates a short bit-string and varies with every item and its position. 4.The function is build in shuch a way that it is very diffivult to generate a different set of entries with same output. 5.Output generated by the function is a short version of the entries itself. 6.In order to add new entries the function is designed in such a way that uses the present value of the contents to generate a new output. The log maintainer issues the log and the output value so that independent parties can verify the correspondence.[8] Forecast: Blockchain Business Value, Worldwide 2017-2030 Gartner’s hype cycle particularly focuses on the set of technologies that are showing potential in achieving a high degree of contentious benefits for the next 5-10 years. The technologies on Gartner’s Inc’s Hype Cycle for emerging technologies, 2016 reveals three distinctive technology trends that are poised to be of the highest priority for organizations facing rapidly accelerating digital business evolution, these include; transparently immersive experiences, the perceptual smart machine age and the platform revolution. These create a relatively new experience with an unmatched level of intelligence in the scenario. . Figure2: Blockchain – Growth Rate Blockchain will undoubtedly affect emerging countries: it can help reduce fraud and corruption and increase legal property titles, which provides entrepreneurial leadership to the world’s poorest. It can also help financial transactions take place more quickly and ensure that aid is distributed with a smaller chance of theft and fraud.[9] Blockchain as a technology which consists of person-to-person networks, Cryptography knowledge and also the consensus in distributed manner. Blockchain helps people to generate trust among those people which are not trusted and with this unison new models will emerge. However, there are certain basic problems with blockchain that comes in between like the increase in the chain affects it and the most important is that the performance of blockchain is that it cannot do the process of transactions as fast as the central system does every second.[10] Governments and other stakeholders will need to address several major challenges before blockchains see widespread use for e-voting. Al-though blockchains are good at rendering security and accuracy, public confidence and trust are necessary ingredients for BEV’s success. Block-chains’ complexity might hinder mainstream public acceptability of BEV. Broadband access and digital user skills are also concerning.[11]A financial management product based on the blockchain technology is suggested in case when you are required to update the information regarding any product in many institutions, also if it is required to manage these wide institutions and also to decrease the delay of the update. It builds a diversified network which is resistant to any damage and gives security for information sharing. In this paper we have used Hyperledger Fabric as the architecture and have studied the tasks of the system which includes the tracing of the product, maintain the route for information etc. To work on the weakness of this architecture we put forward a follow-up prospectus. [12]Blockchain—a kind of distributed ledger technology—has been detailed in the most read press as the next big thing. If I explain in simple words, a blockchain makes it possible to create those digital transactions which are free from alterations and can be shared. To sign transactions among parties this technology uses public-key cryptography. After which the transactions are then created on a distributed ledger. The ledger constitutes a blockchain which has cryptographically linked blocks of transactions (bit.ly/2sgabnq). It is not at all possible or extremely difficult to modify or delete blocks of data that are stored on the block-chain ledger.[13] After the global financial crisis in 2008, everyone is trying to endorse the banking activities or those activities related with money by applying strict rules. But as it is believed that the transactions should be transparent to the general user so that if they are not compatible with the system, they can change it after all they are the big proportion of stakeholders so it is difficult to apply strict rules. Here it has been tried to display how blockchain is the solution out of this situation to ensure the sustainable development. It is already considered that it will be of much help to use blockchain.[14]The blockchain is a peer-to-peer distributed ledger technology that records transactions, agreements, contracts, and sales. Incipiently developed to support crypto-currency, a blockchain can be used for any form of transactions with no intermediary. The benefit of blockchain is that an attacker has to discuss 51% of the systems to overcome the hashing power of the target network. It is therefore not practical to introduce an attack with the motive to affect the blockchain network computationally. The working procedures of blockchain technology is explained in the following example.In today’s scenario as we are aware that hackers are continuously trying to fetch our bank details as a result of which doing an online transaction which involves digital money is a big risk. Crypto-currency like Bitcoin was invented because of the same reason. Blockchain is the technology behind Bitcoin. The blockchain is a public ledger for all the transactions which is completely digital in nature and also has no central power to govern.. On a network of computers, as a data structure.
The basic conception of a blockchain is quite simple: it is a 1. Shared, redundant log file (sometimes called a ledger). 2.The entries are required to be one after the other and should be time-stamped. 3.There is a one way function which generates a short bit-string and varies with every item and its position. 4.The function is build in shuch a way that it is very diffivult to generate a different set of entries with same output. 5.Output generated by the function is a short version of the entries itself. 6.In order to add new entries the function is designed in such a way that uses the present value of the contents to generate a new output. The log maintainer issues the log and the output value so that independent parties can verify the correspondence.[8] Forecast: Blockchain Business Value, Worldwide 2017-2030 Gartner’s hype cycle particularly focuses on the set of technologies that are showing potential in achieving a high degree of contentious benefits for the next 5-10 years. The technologies on Gartner’s Inc’s Hype Cycle for emerging technologies, 2016 reveals three distinctive technology trends that are poised to be of the highest priority for organizations facing rapidly accelerating digital business evolution, these include; transparently immersive experiences, the perceptual smart machine age and the platform revolution. These create a relatively new experience with an unmatched level of intelligence in the scenario. . Figure2: Blockchain – Growth Rate Blockchain will undoubtedly affect emerging countries: it can help reduce fraud and corruption and increase legal property titles, which provides entrepreneurial leadership to the world’s poorest. It can also help financial transactions take place more quickly and ensure that aid is distributed with a smaller chance of theft and fraud.[9] Blockchain as a technology which consists of person-to-person networks, Cryptography knowledge and also the consensus in distributed manner. Blockchain helps people to generate trust among those people which are not trusted and with this unison new models will emerge. However, there are certain basic problems with blockchain that comes in between like the increase in the chain affects it and the most important is that the performance of blockchain is that it cannot do the process of transactions as fast as the central system does every second.[10] Governments and other stakeholders will need to address several major challenges before blockchains see widespread All the transactions done online are, kept in a distributed ledger are created and shared by blockchain. The usage of peer-to-peer network is allowed to use for the transactions. Without the intervention of a central authority the users can make and verify the transactions. The blockchain is merely a database which contains information regarding all the transactions done and is based on bitcoin protocol. III. WORKING OF BLOCKCHAIN The repository for data is a block. Each block contains information, in the case of a bitcoin blockchain, (such as transactions of bitcoin), Block Identifies, Block Header and Merkle Trees. Metadata about a block is contained in Block Headers, such as 1) chronologically before it the cryptographic hash from the block 2) Mining competition 3) to check the transactions in the block Data structure – which is also known as the Merkle Tree Root. To uniquely distinguish the specific block the cryptographic hash is present in the Block identifiers. In the block the differentiation of transactions is present in the Merkle Trees. To build the particular operating structure which is the blockchain, now we are aware of what blocks are so we can combine it together for our use. Explaining it with the bitcoin blockchain example, to identify the prior block in the chain the block header of the next block has a specific field Now the chronological balance is maintained in the chain between the blocks is due to the cryptographic hash in the block header of every block. To protect our digital money with the help of few lines of code blockchain is the best approach. The code that is written is secure as it will be able to work only in a reliable blockchain environment and can be seen only by trusted and authorized users.
Creation the Blockchain: A blockchain Technology is a list of blocks. every block in the BC will have their own digital-signature, contain digital-signature of the preceding Block, and contain a number of data. Below diagram shows the example. Hash = DIGITAL SIGNATURE. Every block does not presently contain the Hash of the Block previous to it, but its own Hash is in division, Calculated from the preceding Hash. If the preceding block/s information is altered then the previous block/s Hash will change in turn affecting all the Hashes of the Blocks there after. Calculating and compare the Hashes permit us to observe if a BC is not-valid. A. Transactions on the Blockchain It is a system in which a particular task is governed by a complete network of computers. The transactions are done with the help of particular special wallets that are organized by specific online companies. A program that gives access to the users to collect and the share their digital coins is a wallet. The wallets are safe as they are protected by the particular ways of encryption that are dependent on the public and private keys that are issued to identified users only. The concept of keys is that suppose if a wallet is encrypted with one user public key then it can only be opened ofr decrypted by the use of the private key of the user this assures the security. Private keys are given to the users and it is unique for their transactions or wallet which can not be obtained back once it is lost.
damage the data within the memory if the data present in the database are present in the hard drive and of a particular computer that is operated by a third party like government and banks. In order that database should be undisturbed the third-party organizations like banks and government recruit a number of people and implement a lot of measures to ensure the same. But in the complete process a fairly large amount of money and time is consumed. There is no risk of fraud to occur as blockchain is an open source manager and therefore each transaction is made available publicly. Now all-day round there are miners who constantly keep track on all the transactions. Now as it is observed by a number of miners which makes it impossible to attempt any fraud.
V. IMPLEMENTATION OF BLOCKCHAIN
TECHNOLOGY
In this part, we are going to overview the implementation method of Blockchain Technology.
1) First, we need to Select a platform Now-a-days a popular network for blockchain is Ethereum. The reason for its popularity is the huge amount of documentation availability and it is also responsive in nature and adapts to the dynamic structure. Blockchain technology assures that the system which user creates will be fully in control of the user, no other person will be able to make changes in them. Now we can run our code by exchanging money, it is done as the authority informs us about an access code which we can use in the given time.
2) The second step is the Initialization of the blockchain You need to create the initial block of the blockchain manually to initialize the blockchain. All the attributes of the blockchain should be present in the first block that you create. Now because of this all the attributes will now be available to all the nodes. A file in JSON format should be created in order to define the initial block. Multiple parameters are required be mentioned: “timestamp” (the authorized time gap between two consecutive blocks), “nonce” (the random value which is at times produced by the cryptographic hash), etc. After you fill in all the details in the JSON file, it is now all dependent on the client whether he wants to create the folder containing the data of the chain and then to initialize it.
3) The third step is to Choose the appropriate consensus protocolHere there are certain questions present in the protocol demanding answers related to some problem of mathematics which involves very huge calculation. If anyone miner is able to find the solution, he gets the right to write the successive block and his solution can be checked by all others. Based on the complete power of the chain the problem’s weight is decided in the dynamic scenario. It is because of this that the blocks need to updated periodically. This ensures that the system is free from any hacking and also the load on network decreases due to the prevention of spam attempts.
4) The fourth step is the execution of your first smart contract “Smart Contract” is the major reason why blockchain is used. It is basically a procedure that executes itself from a specified start value which can be any particular event, date, time, amount. This is the main reason for the success of Ethereum in case of public blockchains.
5) The final step is Debugging and scaling The process of debugging is very complex in case of blockchains. As its execution occurs on the nodes so similar action should be taken on all the blocks and this is what it makes it more complex than a program. First, you should be aware of what blockchain is. The blockchain is a public ledger. This means that it is a public database, in which anyone can join and leave, and also that the system can be read and written by anyone. Furthermore, the system can only be accomplished if many participants are prepared to invest resources in the form of computer capacities and to generate blocks (mining). That is why an incentive must be created to do so. For Bitcoin, this was a profit sharing. The network can be easily succeeded if there are too few members on the network. And if a potential villain controls more than half of the network nodes, he is able to place incorrect data in the blockchain and omit the agreement checks in his network nodes. On the other hand, a blockchain that you run together with friends and partners misses the point.
Here we are reviewing the implementation of BC using Java:
Java-based blockchain was kept simply voluntarily and so, from a users point of view, it only has the functions of sending messages and viewing them in the blockchain, quite similar to a public chatroom. If you want to try the implementation sample then all you need to do is to clone the GitHub project and build it with Maven. Since we also need the infrastructure to communicate with other users, we have to start up a node. This command here shows how it works:
In the above figure shows that compare to normal , regular DB the BC is more effective in the context of Operations, Invariants, Consensus and Replication. In Figure 3: Working procedure of Block-Chain Technology (FLOW CHART): show that transferring money from person ‘A’ to Person ‘B’ in six stages. In Figure2: Blockchain – Growth Rate, In this we can observe that the day by day growth rate of BC. Analyzing all, this technology we can say that BC is a Technology for Future Sustainable Development.
VII. CONCLUSION
A Block-chain is a distributed, de-centralized and the public
digital-ledger i.e. used to register communication across many
computer’s so that any associated documentation can’t be
distorted retroactively, with-out the modification of all
resulting blocks. A blockchain is the structure of data that
represents a financial ledger entry. Every transaction is online
digitally signed to assurance its authenticity and that no one
tamper with it, so the ledger itself and the existing transactions
within it are expected to be of more integrity. Block-chain is
the best way to track the economic transactions which can be
generated to organize not only money related sharing but also
everything that has some worth. This technology uses for
Payment processing and money transfers, Monitor supply
chains, Retail loyalty rewards programs, Digital IDs, Data
sharing, Copyright and royalty protection, Digital voting,
Real estate, land, and auto title transfers. Blockchain
guarantees to solve this problem. And people can easily put
into practice Blockchain-technology using programming
language Java.
REFERENCES
- Michele Marchesi,- “Why blockchain is important for software
developers, and why software engineering is important for blockchain
software (Keynote)” 2018 International Workshop on Blockchain
Oriented Software Engineering (IWBOSE) DOI:
10.1109/IWBOSE.2018.8327564 IEEE March 2018 - Junjun Lou ; Qichao Zhang ; Zhuyun Qi ; Kai Lei -“A Blockchain-based
key Management Scheme for Named Data Networking” 2018 1st IEEE
International Conference on Hot Information-Centric Networking
(HotICN) DOI: 10.1109/HOTICN.2018.8605993 IEEE 15-17 Aug.
2018 - Luo Kan ; Yu Wei ; Amjad Hafiz Muhammad ; Wang Siyuan ; Gao
Linchao ; Hu Kai -“A Multiple Blockchains Architecture on Inter
-Blockchain Communication” (QRS-C) DOI:
10.1109/QRS-C.2018.00037 IEEE August 2018 - VII. CONCLUSION
- A Block-chain is a distributed, de-centralized and the public digital-ledger i.e. used to register communication across many computer’s so that any associated documentation can’t be distorted retroactively, with-out the modification of all resulting blocks. A blockchain is the structure of data that represents a financial ledger entry. Every transaction is online digitally signed to assurance its authenticity and that no one tamper with it, so the ledger itself and the existing transactions within it are expected to be of more integrity. Block-chain is the best way to track the economic transactions which can be generated to organize not only money related sharing but also everything that has some worth. This technology uses for Payment processing and money transfers, Monitor supply chains, Retail loyalty rewards programs, Digital IDs, Data sharing, Copyright and royalty protection, Digital voting, Real estate, land, and auto title transfers. Blockchain guarantees to solve this problem. And people can easily put into practice Blockchain-technology using programming language Java.
- REFERENCES
- Michele Marchesi,- “Why blockchain is important for software developers, and why software engineering is important for blockchain software (Keynote)” 2018 International Workshop on Blockchain Oriented Software Engineering (IWBOSE) DOI: 10.1109/IWBOSE.2018.8327564 IEEE March 2018
- Junjun Lou ; Qichao Zhang ; Zhuyun Qi ; Kai Lei -“A Blockchain-based key Management Scheme for Named Data Networking” 2018 1st IEEE International Conference on Hot Information-Centric Networking (HotICN) DOI: 10.1109/HOTICN.2018.8605993 IEEE 15-17 Aug. 2018
- Luo Kan ; Yu Wei ; Amjad Hafiz Muhammad ; Wang Siyuan ; Gao Linchao ; Hu Kai -“A Multiple Blockchains Architecture on Inter -Blockchain Communication” (QRS-C) DOI: 10.1109/QRS-C.2018.00037 IEEE August 2018
- Florian Wessling ; Christopher Ehmke ; Marc Hesenius ; Volker Gruhn -“How Much Blockchain Do You Need? Towards a Concept for Building Hybrid DApp Architectures” 2018 IEEE/ACM 1st International Workshop on Emerging Trends in Software Engineering for Blockchain (WETSEB) IEEE June 2018
- Kazuyuki Shudo ; Reiki Kanda ; Kenji Saito -“Towards Application Portability on Blockchains”2018 1st IEEE International Conference on Hot Information-Centric Networking (HotICN) DOI: 10.1109/HOTICN.2018.8605977 Aug. 2018
- Dennis Miller-“Blockchain and the Internet of Things in the Industrial Sector” IT Professional ( Volume: 20 , Issue: 3 , May./Jun. 2018 ) DOI: 10.1109/MITP.2018.032501742 IEEE June 2018
- Kazuyuki Shudo ; Reiki Kanda ; Kenji Saito -“Towards Application
Portability on Blockchains”2018 1st IEEE International Conference on
Hot Information-Centric Networking (HotICN) DOI:
10.1109/HOTICN.2018.8605977 Aug. 2018 - Dennis Miller-“Blockchain and the Internet of Things in the Industrial
Sector” IT Professional ( Volume: 20 , Issue: 3 , May./Jun. 2018 ) DOI:
10.1109/MITP.2018.032501742 IEEE June 2018 - Ryan Henry ; Amir Herzberg ; Aniket Kate -“Blockchain Access
Privacy: Challenges and Directions” IEEE Security & Privacy ( Volume:
16 , Issue: 4 , July/August 2018 ) DOI: 10.1109/MSP.2018.3111245
Page(s): 38 – 45 IEEE August 2018 - Hilarie Orman-“Blockchain: the Emperors New PKI?” IEEE Internet
Computing ( Volume: 22 , Issue: 2 , Mar./Apr. 2018 ) Page(s): 23 – 28
DOI: 10.1109/MIC.2018.022021659 IEEE April 2018 - Nir Kshetri ; Jeffrey Voas -“Blockchain in Developing Countries” IT Professional ( Volume: 20 , Issue: 2 , Mar./Apr. 2018 ) Page(s): 11 – 14 DOI: 10.1109/MITP.2018.021921645 IEEE April 2018
- Zhuyun Qi ; Yan Zhang ; Yi Wang ; Jinfan Wang ; Yu Wu -“A Cascade Structure for Blockchain”2018 1st IEEE International Conference on Hot Information-Centric Networking (HotICN) DOI: 10.1109/HOTICN.2018.8605959 IEEE Aug. 2018
- Nir Kshetri ; Jeffrey Voas -“Blockchain-Enabled E-Voting” IEEE Software ( Volume: 35 , Issue: 4 , July/August 2018 ) Page(s): 95 – 99 DOI: 10.1109/MS.2018.2801546 IEEE July 2018
- Bihuan Chen ; Zhixiong Tan ; Wei Fang -“Blockchain-Based Implementation for Financial Product Management” 2018 28th International Telecommunication Networks and Applications Conference (ITNAC) DOI: 10.1109/ATNAC.2018.8615246 IEEE January 2019
- Nir Kshetri-“Can Blockchain Strengthen the Internet of Things?” IT Professional ( Volume: 19 , Issue: 4 , 2017 ) Page(s): 68 – 72 DOI: 10.1109/MITP.2017.3051335 IEEE August 2017
- Quoc Khanh Nguyen-“Blockchain – A Financial Technology for Future Sustainable Development” 2016 3rd International Conference on Green Technology and Sustainable Development (GTSD) DOI: 10.1109/GTSD.2016.22 IEEE Nov. 2016
- Kamanashis Biswas ; Vallipuram Muthukkumarasamy -“Securing Smart Cities Using Blockchain Technology” (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS) DOI: 10.1109/HPCC-SmartCity-DSS.2016.0198 IEEE IEEE Dec 2016
- M. Niranjanamurthy, B. N. Nithya, S. Jagannatha- “Analysis of Blockchain technology: pros, cons and SWOT” Cluster Computing The Journal of Networks, Software Tools and Applications ISSN: 1386-78